
Date: 04 Jun 2025
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common, long-term skin condition that causes inflammation, redness, dryness, and intense itching. It affects both children and adults and can significantly impact a person's comfort and confidence. While there is no permanent cure, eczema can be effectively managed with the right skincare, lifestyle changes, and supportive treatments.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder where the skin becomes hypersensitive and overreacts to irritants or allergens. The exact cause of eczema isn't fully understood, but it is believed to be linked to a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. Individuals with eczema have a weakened skin barrier, making it harder to retain moisture and protect against bacteria or irritants.
Signs and Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms vary depending on the age of the individual and the severity of the condition. Common signs include:
- Dry, scaly, and rough patches
- Redness and inflammation
- Itching (often intense and worse at night)
- Cracked or thickened skin
- Oozing or crusting (in severe flare-ups)
- Skin discoloration after healing
Affected areas typically include the:
- Face and neck
- Elbows and behind the knees
- Hands and wrists
- Ankles and feet
In infants, it often appears on the cheeks and scalp, while in adults, it can become more localized and chronic.
Types of Eczema
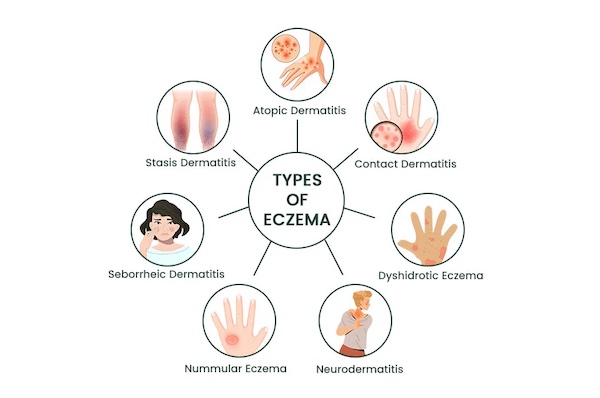
- Atopic Dermatitis
The most common type, associated with asthma or hay fever, usually starts in early childhood and can continue into adulthood.
- Contact Dermatitis
Triggered by contact with irritants (like soap, detergent, or chemicals) or allergens (like nickel or latex).
- Dyshidrotic Eczema
Characterized by small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet.
- Nummular Eczema
Appears as round, coin-shaped spots, usually on the legs or arms.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis
Affects oily areas like the scalp, face, or upper chest, and can cause flaky, yellowish scales.
- Stasis Dermatitis
Occurs in the lower legs due to poor blood circulation and is often accompanied by swelling and varicose veins.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of eczema:
- Family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies
- Environmental irritants (soaps, perfumes, smoke, dust)
- Weather extremes (cold, dry air or hot, humid conditions)
- Stress
- Hormonal changes
- Weakened skin barrier
- Food allergies (especially in children)
Treatment and Management of Eczema Available at Pharmily
Managing eczema involves a consistent skincare routine, avoiding triggers, and using treatments that soothe and repair the skin barrier. Pharmily Kenya offers dermatologist-recommended products that can help alleviate symptoms and support long-term skin health.
✅ Oatveen Soothing Body Wash
- Formulated with colloidal oatmeal, known for its anti-inflammatory and soothing properties.
- Helps relieve itching and irritation during flare-ups.
- Gentle enough for daily use on sensitive or inflamed skin.
- Fragrance-free and ideal for all ages.
✅ Epimol B Moisturising Cream
- Rich in glycerin and emollients that hydrate and restore the skin barrier.
- Reduces dryness and scaling, especially in chronically affected areas.
- Suitable for infants, children, and adults with eczema-prone skin.
- Can be used as a base under topical medications.
Both Oatveen and Epimol B are non-steroidal, making them safe for long-term, daily use to manage mild to moderate eczema and prevent flare-ups.
Lifestyle Tips for Eczema Care
- Use lukewarm water for bathing and avoid harsh soaps.
- Moisturize immediately after bathing to lock in hydration.
- Avoid scratching—keep nails short and wear soft gloves at night if necessary.
- Identify and avoid triggers (e.g., certain fabrics, foods, stress, detergents).
- Wear breathable, cotton clothing to reduce irritation.
- Manage stress through relaxation, mindfulness, or yoga.
FAQs About Eczema
1. Is eczema contagious?
No, eczema is not contagious. It cannot be passed from person to person through contact.
2. Can eczema go away on its own?
In some children, eczema may improve or disappear with age. However, many people experience ongoing flare-ups and will need long-term management.
3. What should I avoid during an eczema flare-up?
Avoid scratching, hot showers, harsh soaps, wool or synthetic fabrics, and any known personal triggers such as allergens or stress.
4. Can diet affect eczema?
Yes. Some people find that certain foods (e.g., dairy, nuts, eggs) can trigger flare-ups. Keeping a food diary and consulting a healthcare provider can help identify sensitivities.
5. How soon can I expect results with Oatveen and Epimol?
With regular use, many people notice softer, calmer skin within a few days. Consistency is key—apply moisturizers and washes daily, even when the skin appears clear, to prevent flare-ups.



