

Date: 11 Aug 2025
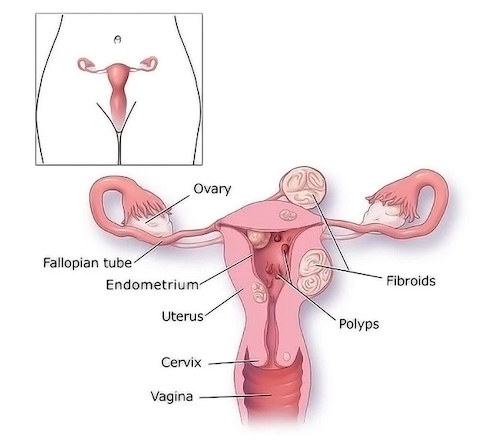
Menorrhagia, commonly referred to as heavy menstrual bleeding, is characterized by unusually heavy or prolonged menstrual periods, typically lasting more than seven days or involving blood clots.
This condition can significantly impact physical health and quality of life, causing fatigue, anemia, and emotional stress.
Identifying the underlying cause, whether hormonal imbalance, uterine pathology, or infection, is crucial for effective treatment.
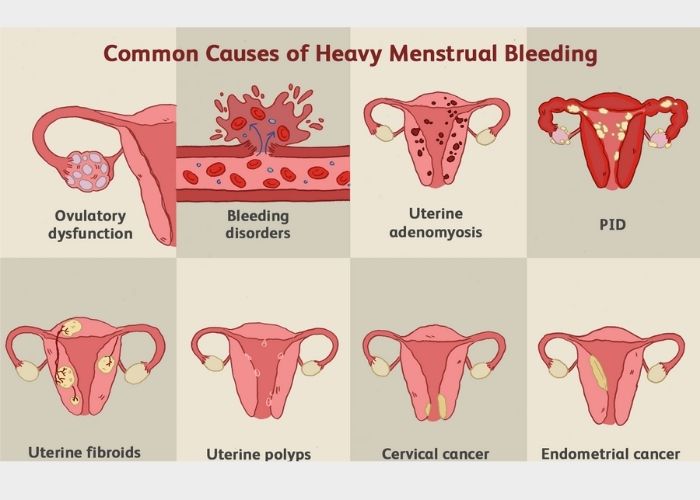
Common contributors to menorrhagia include:
Effective management of menorrhagia depends on addressing the specific trigger:
When fibroids or large polyps are identified, surgical removal—via hysteroscopy, myomectomy, or endometrial ablation—can drastically reduce bleeding. These interventions restore uterine integrity and often provide long-term relief for women experiencing structural causes of heavy periods.
If PID is diagnosed, a treatment course involving broad-spectrum antibiotics is prescribed. Prompt therapy not only resolves infection but also helps stabilize menstrual cycles and reduce excessive bleeding caused by inflammation.
Hormonal dysfunction is frequently corrected using combined oral contraceptives (COCs) or high-dose progestin therapy. These medications regulate the endometrial lining, slow its buildup, and stabilize bleeding. In some cases, intrauterine devices (IUDs) releasing levonorgestrel are used for continuous bleeding control.
Advertisements complement core treatments:
These pharmacy products offer supportive care during the treatment of heavy bleeding:
A highly absorbable, stomach-friendly iron supplement ideal for managing anemia due to menorrhagia. Its liposomal delivery ensures higher uptake with minimal gastrointestinal side effects.
Iron bisglycinate is known for its superior absorbability and tolerability. Formulated with Vitamin C, B12, and folic acid, this supplement helps rebuild healthy blood levels and combat fatigue. Why it stands out: Specifically designed for iron deficiency and especially helpful for women with heavy menstrual bleeding.
This liquid iron formula is flavored and easy to take, ideal for those who dislike pills. Enriched with B vitamins and minerals, it supports red blood cell production and energy. Why it stands out: Delicious flavor, gentle on the stomach, and ideal for ongoing supplementation during treatment.
Here’s how you can combine medical treatment with supportive supplements:
Consult your healthcare provider if:
Menorrhagia can significantly affect physical and emotional health, but targeted treatment based on cause, combined with supportive supplements, can restore balance and wellness.
Surgical or medical interventions correct structural or infectious issues, while hormonal therapy regulates bleeding. Iron supplementation, particularly gentle, high-absorption formulas from Pharmily Kenya, supports recovery by preventing anemia. The option of tranexamic acid aids in reducing blood flow during treatment.
By taking a structured, informed approach, women experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding can regain vitality and reclaim control over their lives.